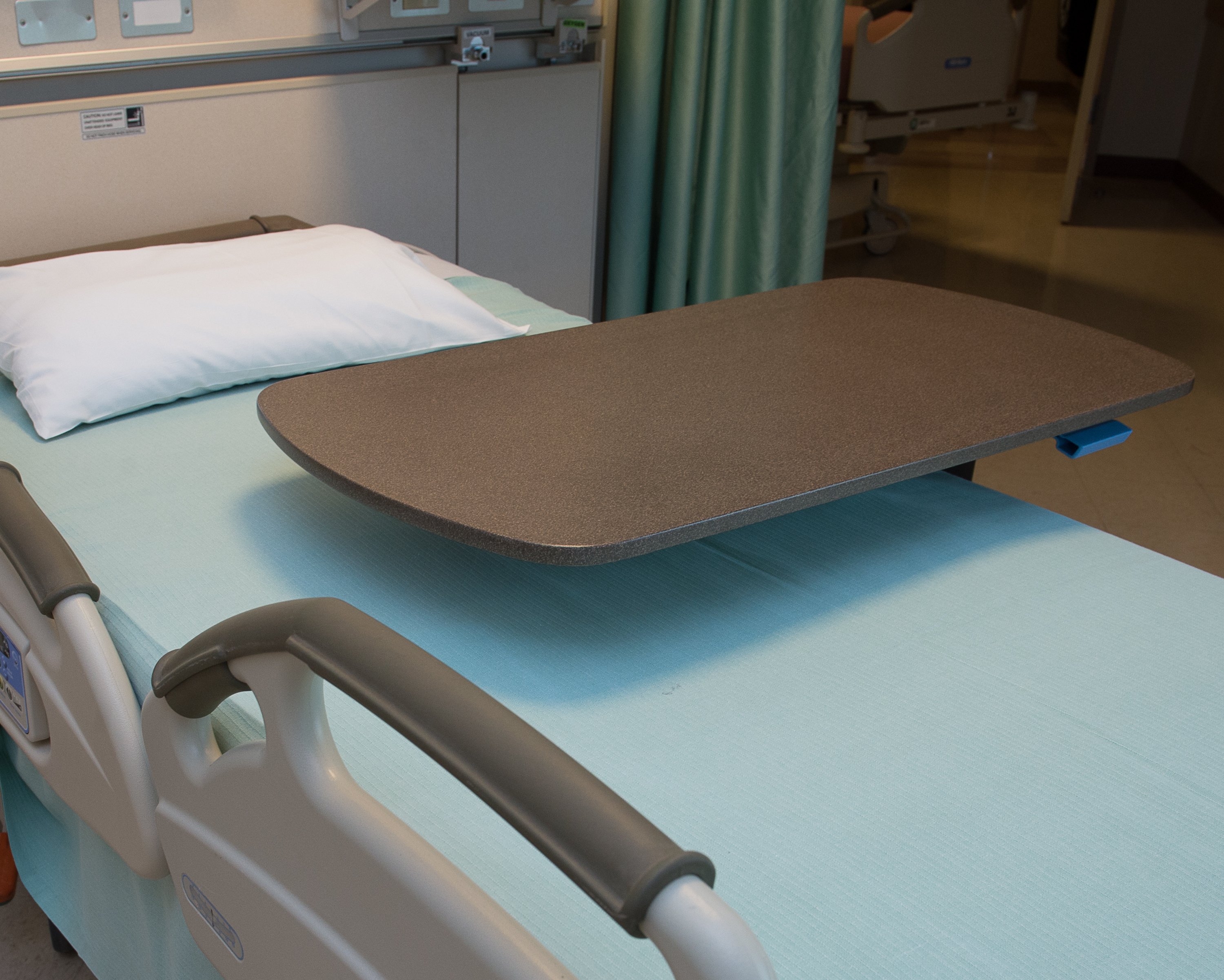
In June 2016, EOS Surfaces officially entered into a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement (CRADA) with the Central Texas Veterans Health Care System (CTVHCS) in Temple, TX. A CRADA is a legal “contract” that provides an exciting opportunity for NIH researchers to join with partners from private industry and academia in a collective effort to achieve shared research goals. CRADAs aim to promote collaboration across governments, universities, and the private sector to expedite the transfer of innovative, effective, proven, and beneficial technologies to the marketplace. The ongoing study of EOScu under principal investigator Dr. Chetan Jinadatha at the Olin E. Teague VAMC will further test the material’s efficacy in reducing both the bioburden of a patient room and incidents of hospital acquired infection (HAI) while also performing the first known parallel analysis of the positive economic impact of such reductions.
CENTRAL TEXAS VETERANS' HEALTHCARE SYSTEM
OLIN E. TEAGUE VETERANS’ MEDICAL CENTER
Recipient of multi-year R01 grant to evaluate efficacy and economic impact.
Early Results from Ongoing EOSCU Clinical Trial at the
Olin E. Teague Veterans’ Medical Center
What is bioburden?
Bioburden is the number of viable microorganisms that can be found on a surface, in a sample, or in a solution before sterilization.
What are HAIs?
Hospital-associated infections, or healthcare-associated infections, are infections that patients get as a direct result of receiving care in a medical facility.
What is statistical significance?
If results are statistically significant, this means that it is very unlikely that the results are due to chance.

About the clinical trial
The trial was launched in October 2016 at the Olin E. Teague Veterans’ Medical Center (VAMC), part of the Central Texas Veterans’ Healthcare System, located in Temple, Texas.
As one of the largest healthcare systems in the US, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) provides essential care to more than 8.7 million veterans in 300 VA hospitals, as well as 827 community-based outpatient clinics. Veterans are particularly vulnerable to HAIs and as a result, VA has made infection prevention a top priority. Its Health Services Research & Development Service (HSR&D) has conducted several studies focused on detecting and preventing HAIs.
The facility outfitted all 120 patient rooms with EOSCU Preventive|Biocidal Surfaces™ including all countertops, over-the-bed tables and bed rails in the facility. The purpose of the study was to measure the additional protection against bacterial infection above and beyond existing infection control protocols, including reductions in contamination (bioburden) and reductions in HAI rates. The first phase of the study confirmed bioburden reduction while the second phase confirmed statistically significant reductions in HAIs. You can download the studies here.
The investigative team recognized EOSCU had potential to become a standard of care, and therefore submitted data from the first study as a part of a R01 application, which was approved. See here for more information.
The ongoing study continues to result in data confirming the efficacy of the EOSCU surface on both HAI rates, bioburden, and economic impact. Even during the COVID-19 pandemic, which occurred while the studies were underway, statistically significant reductions were measures despite the radical changes it experiences. Under the R01 grant, ongoing data collection aims to isolate the specific economic benefits of the infection reductions due to EOSCU.
The ongoing research will evaluate potential financial impacts of a biocidal material on a healthcare facility. This type of data will reveal the way EOSCU can help save lives and money.
R01 Timeline
IDWeek 2023 Poster Presentation
Demonstrated efficacy against C. difficile spores and infection rates
IDWeek 2022 Poster Presentation
Demonstrated reductions in HAIs and bioburden despite ongoing global pandemic. Poster found here.
COVID-19 Pandemic
First NIH Study Published
NIH R01 Grant Awarded
Initial Study Published
Clinical Study Launched
Investigation underway at Central Texas VA.
CRADA
Preliminary work to draft and establish CRADA.
![EOScu Logo - Dark - Outlined [07182023]-01](https://eoscu.com/hubfs/Eoscu_June2024/Images/EOScu%20Logo%20-%20Dark%20-%20Outlined%20%5B07182023%5D-01.svg)